If you apprehend the operation method of cryptocurrency mining, you will recognize that miners will dig out a new block after calculation, and different miners will proceed to calculate from the result after a new block is born. However, when two miners mine a block at an identical time, two one-of-a-kind consequences may additionally occur. Therefore, different miners will have greater than one block to track, and if this continues, two unique blockchains will be formed. This state of affairs is the so-called “fork”.
What is a “FORK”
However, “FORK” is typically considered as a “temporary inconsistency phenomenon”, the state of affairs will now not be ultimate for too long, and will sooner or later be resolved through the addition of extra and greater blocks. The cause is that miners will have a tendency to attain a consensus, pick out a blockchain with a longer improvement and proceed to operate and reproduce the authentic effects of the longer blockchain, so the blockchain will nonetheless have a tendency to the identical to one in the end. Not simply Bitcoin, forks in the blockchain can appear in any cryptographic technological know-how platform, and this is due to the fact blockchains and cryptocurrencies work in essentially the equal way no be counted which cryptographic platform they are on.
The “forks” that show up on the blockchain community are generally brought on through “delays in the transmission of statistics in the network”. Due to community pace transmission delays inflicting blocks to be out of sync, “forks” appear all the time. When there is an exchange in the blockchain due to “consensus”, the nodes will be divided into two versions: “updated” and “not but updated”. The chain forks into two chains.
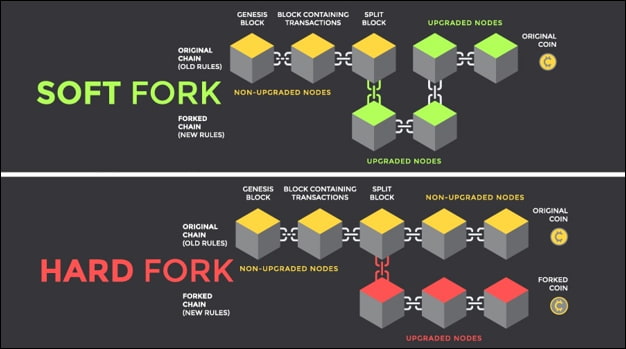
“Hard Fork”
“Fork” can additionally be divided into “hard fork” and “soft fork”, however, the two are the same. A tough fork is a radical improvement that makes preceding transactions and blocks legitimate or invalid and requires all validators in the community to improve to a more modern version, due to the fact miners on the ancient chain can’t acquire miners on the new chain. blocks. In this case, there are solely two outcomes. The first state of affairs is that the miners take delivery of the update, proceed to function in a massive chain, and whole the replace of the blockchain. The 2d state of affairs is that the miners do now not receive the update, insist on persevering with using the historical chain and keep a positive quantity of miners to proceed to hold the operation of the historical chain. Eventually, the chain will fork absolutely and create a new foreign money known as a “forked coin”. Among them, Ethereum is a desirable example. To make changes easier, Ethereum in the main makes use of challenging forks to replace the shape and policies of Ethereum.
“Soft Fork”
Compared with tough forks, gentle forks are less difficult to gain stability in consensus. Under the tender fork, even if a new model appears, the customer on the ancient model can nonetheless change in accordance with the policies on the historical chain. Under this consensus, it is now not fundamental to regulate the whole chain thru forks, and solely want to add some new guidelines to make the ancient and new chains compatible. The gentle fork is conducive to the non-stop and secure use of the present-day situation, and it is an accurate factor for some human beings who do now not desire to alternate the repute quo. However, because the gentle fork desires to take into account the operation of the historic chain, there is constrained room for improvement; on the contrary, the tough fork no longer wants to take into account the traits of the historic nodes, and the variety of updates and changes can be greater.
A gentle fork is a gradually improve mechanism. A smooth fork takes place every time a majority of individuals take part in the upgrade. Using the Bitcoin blockchain as an example, when the new device mandates a block dimension exchange from 1,000KB to 800KB, non-upgraded miners can nonetheless test to see if the new transaction is valid. However, their mining work can also be rejected using the blockchain network. As the miners of the authentic block recognize that their block was once rejected, they will step by step pick to upgrade. As greater miners upgrade, the unique block will be orphaned. As a result, the complete block ecology can be up to date in a gentler way.