
Bitcoin Addresses
In the quest for better technology, some ancillary things inevitably get a little confusing. While the way bitcoin addresses are formatted has changed a lot, it’s really not something the average person needs to care about. Bitcoin has used multiple standards, and sometimes multiple standards at the same time, over the past few years, which makes these weird strings all the scarier and overly scary.
The different types of Bitcoin addresses are basically cross-compatible, meaning that funds on any one type of address can be sent to any other type of address. If you’re having trouble sending funds to a certain address, it’s most likely an issue with your wallet client, just try upgrading your wallet to support the address types described below.
Generally speaking, the wallet software you use will manage addresses for you and prevent you from sending funds to an invalid address. However, various wallets may not do so consistently. The Trezor Suite app recently released a public beta version, which prevents you from sending money to invalid addresses, also supports all commonly used address types, and helps you avoid overpaying fees; this last problem in the popular wallet software is common, especially during times of high network traffic.
What do the different types of Bitcoin addresses look like?
To comfortably send and receive bitcoins, you need to know two things: how to identify a valid address, and which type of address you should use.
Most of the time, you should prefer to use native Segregated Witness addresses (also known as “Bech32 addresses“), which always start with bc1. This kind of address is the best, because it uses the most efficient data when constructing a transaction, so the handling fee is also the lowest, because the handling fee of Bitcoin is priced according to the amount of data in the transaction.
The original segregated witness Bech32 address looks like this:
bc1qj89046x7zv6pm4n00qgqp505nvljnfp6xfznyw
However, not all wallet software supports the Bech32 format now. A more common address format is the “Pay to Script Hash (P2SH)” address, also known as “Nested Segregated Witness Address”. From the perspective of transaction fees, it is also more efficient than traditional address types, and can be recognized at a glance because it starts with 3. If you are not sure whether the destination address your transaction is sending to supports segwit, then nested segwit addresses generally support it.
The isolated witness P2SH address looks like this:
3EmUH8Uh9EXE7axgyAeBsCc2vdUdKkDqWK
If you are using older wallet software, you may need to use traditional Pay to Public Key Hash (P2PKH) addresses. It is called a legacy address because it is considered a remnant of earlier technology. Generally speaking, the handling fee of this kind of address will be higher, but it is still universal. You can tell if an address is a P2PKH address by whether it starts with 1.
The traditional P2PKH address looks like this:
1MbeQFmHo9b69kCfFa6yBr7BQX4NzJFQq9
You should develop the habit of checking the target address every time you initiate a transaction to ensure that the target address has not been tampered with. Although the beginning of the address can help you identify the type of this address, the length of the address will also vary with the type. Bech 32 addresses have 42 characters—the newest address type—while P2SH and P2PKH addresses are only 32 characters.
What are valid bitcoin addresses to receive funds?
All your types of addresses are derived from the same source, your mnemonic (also called “seed word”). Below is an example of a seed word from which all three types of addresses can be derived:
gentle melt morning mother surprise situated lens beef cloud inquiry genuine feel
With the seed phrase, you can create a valid Bitcoin receiving address, of any type, as long as your wallet software supports it. With Trezor Suite, any of these types of addresses can be generated with just a few mouse clicks.
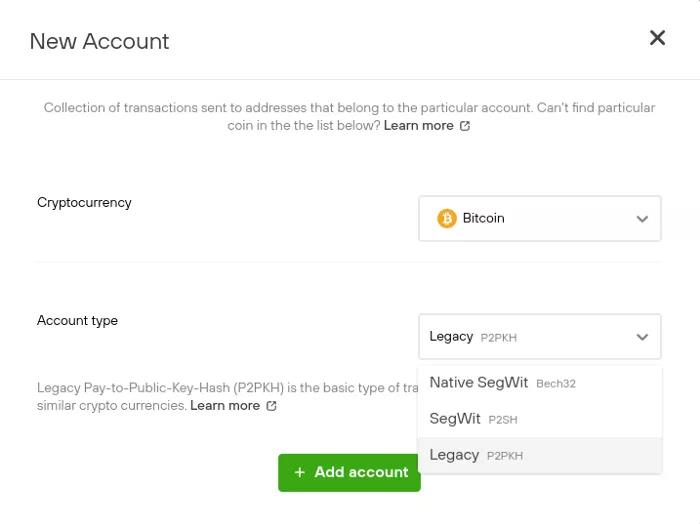
– On the “Account” page use the sidebar menu “Add New Account”-
Because of the characteristics of Bitcoin development and upgrades, you may encounter more address types over time, but the addresses are all backward compatible. A Bech32 address can send funds to a P2SH or P2PKH address without any worries. The reverse is also possible, you can also use traditional addresses to send funds to Bech32 and P2SH addresses; however, if you are using older wallet software, the software may not recognize Bech32 and P2SH addresses, so you are prevented from sending funds, even if this There’s a good chance the deal will go through. It’s just a problem with the outdated protection mechanism, not Bitcoin. You just need to upgrade the software and the transaction will go through.
When in doubt, you can rest assured to use a traditional address because it has the broadest support. While the wallet software you use may place some limitations on you, as long as it allows you to sign and send transactions, you have nothing to worry about. Bitcoin addresses are cross-compatible, and each type of address can send funds to any type of address. For the best flexibility, and the least confusion, upgrade to Trezor Suite, where you have full control over any kind of address.
Why do address types keep changing?
Among the address types explained here, both P2SH and Bech32 types are related to the upgrade of Segregated Witness. Segregated Witness is an upgrade of the transaction format, which allows more transactions to be placed in a block, which can improve the throughput of the network. This also means that the benefits provided by SegWit can only be enjoyed if the transaction is initiated from a SegWit-compatible address (such as P2SH and Bech32 addresses); and the type of receiving address does not matter. From a privacy standpoint, it is important to ensure that the remaining cryptocurrency in the transaction is returned to the same type of address (as the sender). Trezor Suite will handle it for you automatically.
How to get a bitcoin address
Newcomers may be confused about how to get an address to collect money from. It’s very simple, you just need to download a wallet software, such as listed in this recommended list. The wallet software will generate a mnemonic for you, and use this mnemonic to generate available addresses and display them to you. A better practice is to use each address only once, whether it is receiving or sending money. Because a mnemonic can generate countless addresses, you don’t need to worry about insufficient addresses, and this approach will provide you with additional privacy protection.
If you have a Trezor hardware wallet, you can use the Trezor Suite desktop software to create and manage Bitcoin addresses. The mnemonic words used in these addresses are generated and kept in your Trezor hardware, so others cannot see them Your mnemonic cannot copy your wallet. You can also generate a new address for each transaction directly in Suite.
Find your Bitcoin receiving address
If you want to send bitcoins to your own wallet, you need to determine your receiving address. In Trezor Suite, you need to select the account you want to receive funds from and click the “Receive” button. Then you can see a list that contains the active addresses you generated before, as well as a preview of the latest unused addresses. Click “Show full address” to see the latest unused billing address. After clicking, please check that the address displayed on the screen is consistent with the address displayed on your hardware wallet device, then you can copy and send this address to the person who sent you the bill.
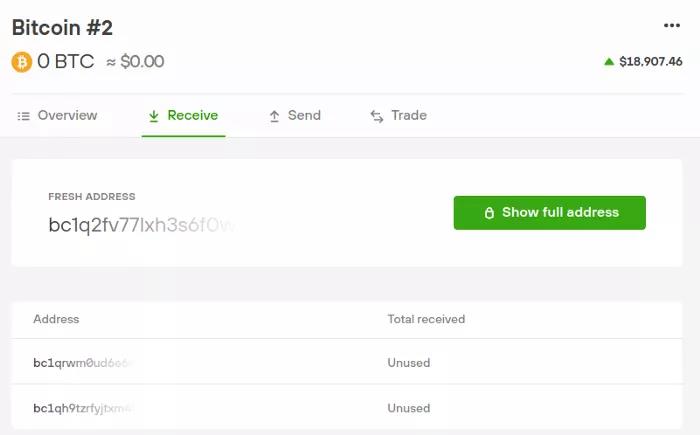
As you can see, here we use the Bech32 address starting with bc1, but unless the sender also uses a Bech address or P2SH address, they cannot enjoy the benefits of low transaction fees provided by SegWit. Always use Bech32 addresses to send accounts to save transaction fees.
If this is your first time collecting accounts, it is recommended that you send a test transaction before transferring all funds in; Certainty. Try to send a small amount of bitcoin (such as the amount in Satoshi) to test your receiving address, and wait patiently for the confirmation of this test transaction before you send more funds in.
How to send bitcoins to an address
When you need to pay someone bitcoin, you just need to get the receiving address provided by the other party. With Trezor Suite, just move to the “Send” column on the account page, enter the address of the other party, and then, you also need to check that the characters in the text box are consistent with the address you got at the beginning, because there is always a chance that your computer clipboard be hijacked by malware.
After entering the address, set how much handling fee you are willing to pay for this transaction. Higher fees will encourage miners to package your transaction first, so the other party will receive the account faster. In the picture below, we are using the highest transaction fee suggested by Trezor Suite, in order to get the transaction on-chain within 10 minutes (this is the fastest that the Bitcoin network can do).
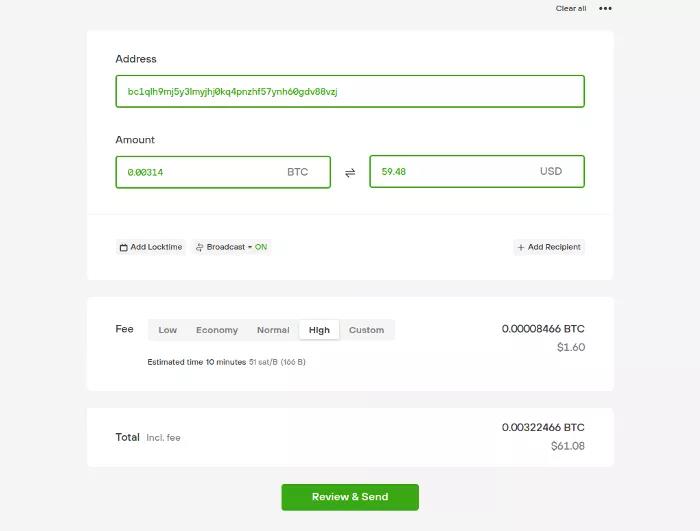
It is good practice to check the commissions you pay. The automatic settings of some wallet software will greatly overestimate the transaction fee. Even during busy times, you’ll only pay a few dollars, not much more. If the fee suggested by the wallet is too high in your opinion, you can look for advanced options and enter a value yourself.
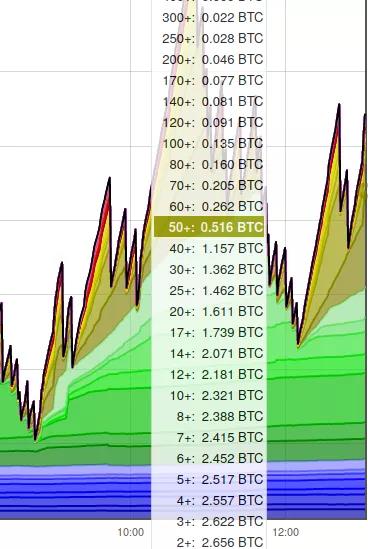
There are many tools on the Internet that can help you see how high the transaction fees are paid by users who are sending transactions, such as the second picture on this website. As you can see in the figure below, most of the transaction fees paid by exchanges are lower than 50 Satoshi/byte, so the 51 Satoshi/byte suggested by Trezor Suite should be able to be uploaded to the chain within 10 minutes.
How to get back bitcoins sent to wrong address?
In most cases, bitcoins sent to the wrong recipient cannot be retrieved if it is an invalid address.
In rare cases, if you know who the target address (effective address) of your transaction belongs to, you can try to contact him, and if you are lucky, TA will be willing to send the funds back to you.
If neither method works, the last resort is to use OP_RETURN to send a message to the address of the accidental payment, describe your mistake and ask the other party to return it in good faith. This is also very likely to fail, so the way to prevent you from sending funds to the wrong address is always, check check check, double check that the transaction is going to the wrong address before you hit send.
The sad truth is that while many wallet software do a good job of identifying valid addresses, there are still users who send funds to the wrong type of address, such as sending Bitcoin to a Litecoin address. This error, some wallets are Can’t check it out.
In this case, the network cannot recognize that this is an erroneous transaction, because from the perspective of the wallet, the form of this transaction is no different from other transactions, and it is also a valid transaction. In this case, whether you can get your funds back depends on which network the address you fill in belongs to. If you sent funds to a Litecoin address, as long as you have the private key to the receiving address, you should still be able to get your bitcoins back (even if it was a Litecoin address). But if you don’t have the private key to that address, the chances of getting it back are pretty much nil. If that happens, you’re left with the consequences. Also, remember to switch to a better wallet.




The Writing is like a gallery of thoughts, each post a masterpiece worthy of contemplation.
The passion for this subject is infectious. Reading The post has inspired me to learn more.
Beautifully written and incredibly informative, The post has captured my attention as if it were a love letter written just for me.
Refreshing take on the subject, like a cold splash of water to my long-held beliefs.
Most comprehensive article on this topic. I guess internet rabbit holes do pay off.
Amazed by The knowledge breadth, or what I’ve been mistaking for just good Googling skills.
The consistency and high quality of The content are something I really appreciate. Thank you for The dedication.
A breath of fresh air, or what I needed after being suffocated by mediocrity.
A masterpiece of writing! You’ve covered all bases with elegance.
Remember, the key with flirtatious comments is to keep them light-hearted, respectful, and ensure they’re taken in the spirit of fun and admiration.
The post was a beacon of knowledge. Thanks for casting light on this subject for me.
The finesse with which you articulated The points has me captivated. It’s as if you’re speaking my language.
Reading The work is like gazing at a masterpiece; every detail contributes to a breathtaking whole.
The elegance of The prose is like a fine dance, each word stepping gracefully to the next.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
I genuinely learned something new today. Fantastic post!
This post is bursting with value — amazing!!
This post was incredibly uplifting and informative.
Your content always brings fresh insight.
This article bursts with life and inspiration — beautiful!
I love how thoughtful and well articulated this is.
You have a remarkable way of connecting ideas.
I appreciate the generosity in your writing — you always share so much value.
I’m genuinely in awe — this is exceptional!
This post is a perfect example of quality content.
You write with so much intention and clarity.
I’m saving this — too good not to revisit!
This post is a perfect example of quality content.
I’m genuinely in awe — this is exceptional!
This should be the standard for exciting writing — brilliant!
Your writing never fails to impress me.
I appreciate how you approach topics with such sincerity and detail.
This was overflowing with positivity and energy — loved it!
This article had my full attention — amazing writing!
Your writing never fails to impress me.
I appreciate the positivity and insight you bring to your writing.
Completely captivated from beginning to end — amazing!
You write with such spark — I’m genuinely impressed!
finish because the clarity, structure, and passion in your writing
finish because the clarity, structure, and passion in your writing
create an experience that feels both educational and inspiring. Every
You’ve created something vibrant and exciting — amazing job!
how effectively you communicate your ideas, and this piece genuinely
This pumped me up in the best way possible!
You absolutely crushed it with this one — WOW!
The level of insight in this post is outstanding.
Such a powerful and well-written post.
Your writing radiates excitement — wonderful job!
This post just made my morning.
Your writing always inspires me.
You always bring clarity to confusing subjects.
Such a beautifully expressed and insightful article.
This article had my full attention — amazing writing!
This was extremely well written and very helpful.
This is adrenaline in written form — AWESOME!
Your point of view is so refreshing.
This made a real impact on me — thank you!
The excitement in this post is contagious!
I appreciate how engaging and informative this was.
Your insight is always incredibly valuable.
This was exceptional — keep up the amazing work!
This was written with such clarity — thank you!
You’ve set the bar incredibly high — WOW!
Your perspective here is so valuable.
Your enthusiasm makes this post unforgettable!
This was one of the best reads I’ve had in a while.
This was incredibly eye-opening — thank you!
This was refreshingly exciting — loved it!
This was one of the best reads I’ve had in a while.
You’ve got an amazing ability to simplify things.
Thank you for sharing something so thoughtful and well crafted.
This post is absolutely glowing with passion!
Such a beautifully expressed and insightful article.
Your content always brings fresh insight.
This made me feel genuinely motivated — thank you!
You have a real talent for breaking down complex ideas.
This post shines with passion and energy — fantastic!
You always deliver top-notch content — keep it up!
This post was incredibly well structured.
This post was a joy to read — thank you!
Everything about this post screams excellence!
This was such an energizing read — loved it!
The quality of your writing is outstanding.
Your posts always give me something valuable to think about.
This was incredibly eye-opening — thank you!
The excitement in this post is contagious!
There’s so much life in your writing — incredible work!
You’ve turned content into an experience — amazing job!
You absolutely nailed the tone — energetic and sharp!
This is content worth celebrating — phenomenal job!
I can’t believe how much I loved this — fantastic job!
I really appreciate your thoughtful approach to writing.
Your ability to excite readers is unreal — fantastic job!
You’ve crafted such a thoughtful and detailed piece.
You write with so much intention and clarity.
This made me feel genuinely motivated — thank you!
You communicate ideas better than almost anyone else I follow.
Your talent is showing BIG TIME — wow!
I can’t get over how enthusiastic and uplifting this is — WOW!
Your perspective here is so valuable.
This made my day — thank you for sharing!
You communicate ideas with so much ease and clarity.
You consistently offer such high-quality information.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://www.binance.info/ES_la/register?ref=VDVEQ78S
refreshing depth of insight. I found myself fully engaged from start to
create an experience that feels both educational and inspiring. Every
point resonated strongly and was presented beautifully. It is remarkable
Your enthusiasm makes this post unforgettable!
I walked away with so much value from this.
This is real quality content — thank you!
This post really exceeded my expectations.
I feel more informed after reading this.
You’ve injected so much enthusiasm into this — amazing!
I’m absolutely loving the vibe here — great work!
This was written with such clarity — thank you!
This is real quality content — thank you!
Brilliant!! I’m so glad I clicked this!
This had so much energy — I absolutely loved it!
I love how engaging and informative this was.
Your enthusiasm is magnetic — I love it!
You really know how to make a topic come alive.
You’ve turned content into an experience — amazing job!
Excellent post — concise, clear, and thoughtful.
You make learning so enjoyable — thank you!
This is content worth celebrating — phenomenal job!
This is real quality content — thank you!
This post was full of helpful information.
This was both insightful and enjoyable — perfect combination.
I can’t get over how enthusiastic and uplifting this is — WOW!
You approach topics with such grace and intelligence.
You have a remarkable way of connecting ideas.
I’m blown away by the value in this post.
I really appreciate your thoughtful approach to writing.
The enthusiasm here is off the charts — well done!
This is the kind of content that keeps me coming back.
I’m genuinely in awe — this is exceptional!
Wow!! I’m honestly amazed by how good this was!
I can’t praise this enough — outstanding work!
Such a dynamic and exciting piece — I’m impressed!
You always deliver top-notch content — keep it up!
You’ve delivered another gem — well done!
This was such a fun and energetic ride — loved it!
I’m honestly amazed at how fun this was to read!
I love how thoughtful and well articulated this is.
This article was impressive in every way.
I’m honestly amazed at how fun this was to read!
The level of insight in this post is outstanding.
The energy here is unmatched — you crushed it!
You’ve made this topic far more understandable — thank you!
This should be the standard for exciting writing — brilliant!
This is the kind of content that makes a real difference.
Every sentence bursts with enthusiasm — love it!
Your energy in this post is infectious — LOVE IT!
I appreciate how thorough and well researched this is.
This might be your most exciting post yet — WOW!
This was smart, helpful, and beautifully written.
This might be your most exciting post yet — WOW!
You’ve crafted such a thoughtful and detailed piece.
This had so much energy — I absolutely loved it!
Wow!! I’m honestly amazed by how good this was!
Another excellent post — you never disappoint!
You have such an authentic and compelling voice.
This lit a fire in me — THANK YOU for this energy!
I’m walking away energized — thank you for this amazing content!
Everything about this post radiates excitement — loved it!
This article helped me understand things from a new angle.
This post feels alive — seriously impressive work!
Your energy is a breath of fresh air — fantastic post!
This was one of the clearest explanations I’ve seen.
You’ve got an extraordinary gift for writing energetically — wow!
Your writing sparks so much excitement — loved it!
This was both insightful and enjoyable — perfect combination.
This article had my full attention — amazing writing!
You’re on FIRE with content like this — amazing job!
You’ve got a gift — this is stellar!
I can’t stop smiling — this post made my day!
You’re becoming one of my favorite writers online.
You always deliver top-tier writing.
This hit me with pure positivity — THANK YOU!
This was such a meaningful and insightful post.
This post shines with passion and energy — fantastic!
This is the kind of content that makes people fall in love with learning!
This post was absolutely fantastic from start to finish.
You’ve turned this topic into something thrilling — impressive!
Such a powerful and well-written post.
Your posts always give me something valuable to think about.
Your explanations are always spot-on.
You’re raising the bar with posts like this.
Another excellent post — you never disappoint!
I admire the clarity and confidence in your writing.
You have an incredible ability to inspire and excite!
Your voice is powerful, clear, and so inspiring!
This writing feels like a celebration — wonderful job!
I can’t get over how good this is — seriously impressive!
Your writing is always so thoughtful and authentic.